This talks about some basic steps for getting started with Git repositories in Visual Studio 2017. This doesn’t talk about overall usage, but rather just how to get some things setup.
Visual Studio 2017 already comes with basic support for Git. In this post I’m using Visual Studio 2017.3.3.
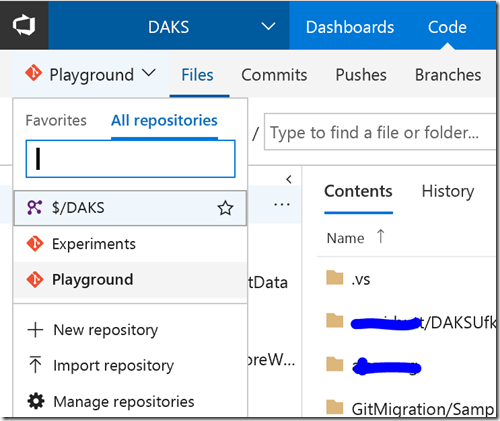
The first think I did was create a Git repository (repo) in VSTS (Visual Studio Team Services). You can see the + New repository option in the image below. I created the one called Playground.
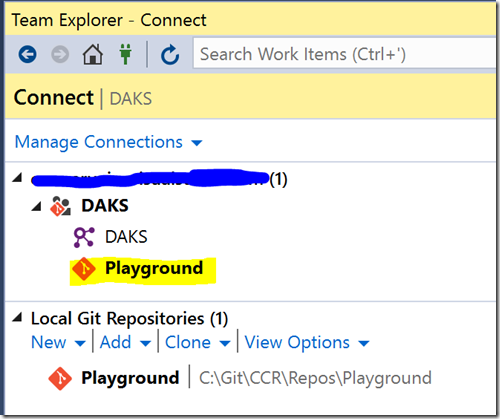
After that I connected to that Repo and Cloned it.
After connecting to a Git repo then I see this on the Team Explorer tab:
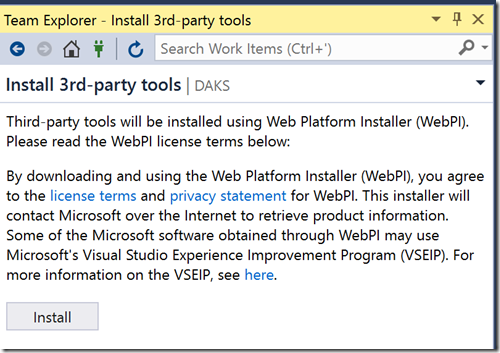
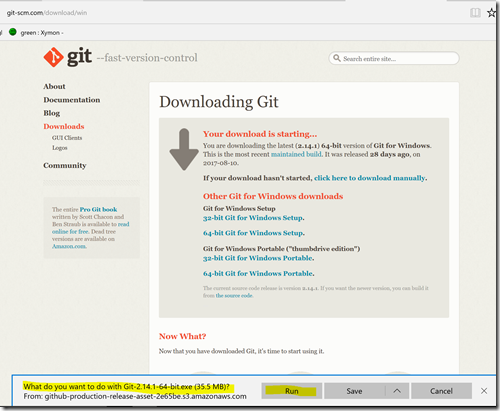
When I click on Install, I see this disclaimer:
Then clicking that install, I go to a page that seems to download the right version for my by just landing on the page. I pressed Run.
Then when the Install started I clicked Next 9 times (took the default each time).
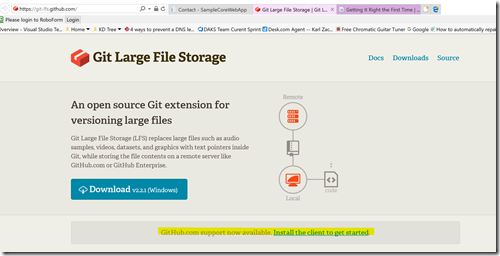
I then went to this page to get Git LFS: https://git-lfs.github.com/
And I clicked the similar link:
After that I did a Sync with the VSTS repo and all was well. Ok… That’s a lie. This process caused some local changes so the pull didn’t work. I had to do to the command prompt and type “git checkout .” to undo all the changes (3 of them) to my local copy. Then the Sync worked.
Some key notes…
– I had already added the items I wanted to track from another machine and committed those changes to the remote (VSTS) repo.
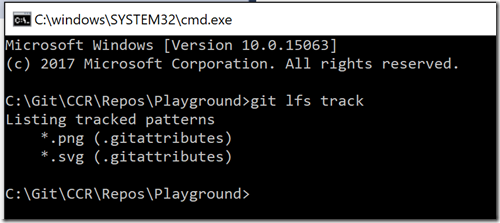
– If this is your first machine for the project that is using git LFS then you will need to run the track command to add them. As you can see, if I run just “track”, it shows which items I’m tracking with LFS:
You can add other files by running the git lfs track command, for example:
git lfs track “*.png”
adds the right information to the .gitattributes file.
Leave a Reply